Show how you would accomplish each of the following synthetic conversions.
a. trans-but-2-ene → trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane
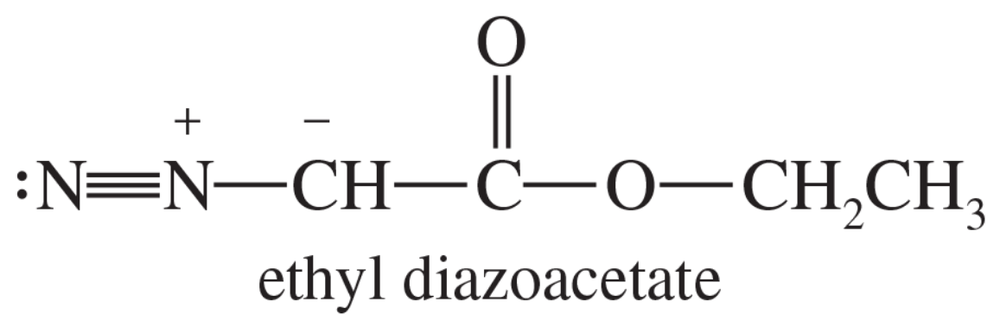
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: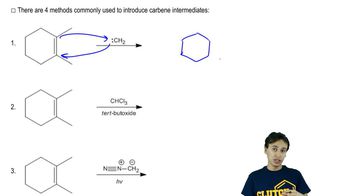

 1:49m
1:49mMaster General properties of cyclopropanation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning