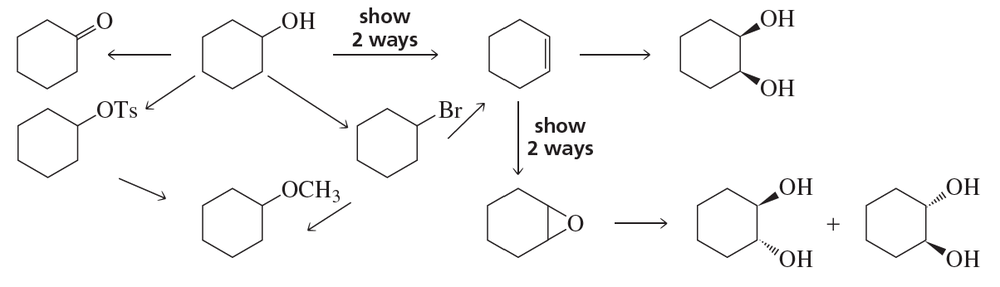
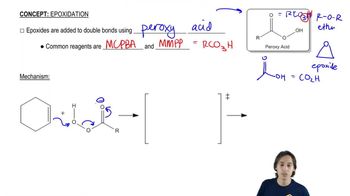
One way to think about concerted reactions is to imagine them as being stepwise reactions where, besides the slowest step, all others have infinitesimally small activation energies. Considering the hypothetical stepwise mechanism and actual concerted mechanism of epoxide formation, show what a reaction coordinate diagram might look like for each possibility.
(a) Stepwise, hypothetical mechanism: