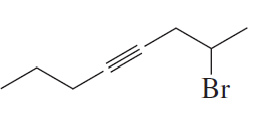
Textbook Question
Which of the following names are correct? Correct those that are not correct.
a. 4-heptyne
b. 2-ethyl-3-hexyne
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 1:55m
1:55mMaster How to name alkenes and alkynes with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning