Which of the following C-terminal peptide bonds is more readily cleaved by carboxypeptidase A? Explain your choice.
Ser-Ala-Leu or Ser-Ala-Asp
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: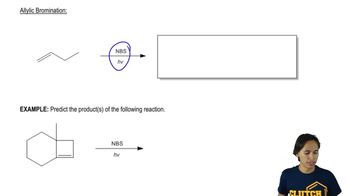


 9:34m
9:34mMaster Peptides and Polypeptides with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning