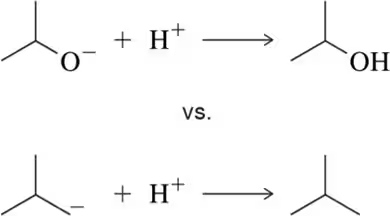
For the following reactions we have not seen yet, which side, if either, would be favored by increasing the temperature?
(c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 5:02m
5:02mMaster Breaking down the different terms of the Gibbs Free Energy equation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning