cis-4-Bromocyclohexanol and trans-4-bromocyclohexanol form the same elimination product but a different substitution product when they react with HO−.
a. Why do they form the same elimination product?
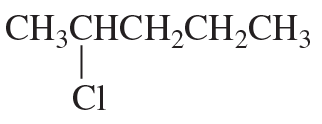
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: