Four pairs of compounds are shown. In each pair, one of the compounds reacts more quickly, or with a more favorable equilibrium constant, than the less conjugated system. In each case, explain the enhanced reactivity.
(d)
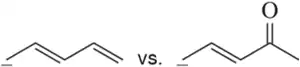
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 3:15m
3:15mMaster Why we need factors affecting acidity and when to use them. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning