Textbook Question
Draw the structure that corresponds to the name provided.
(d) (2R,4Z)-5-bromopent-4-ene-1,2-diol
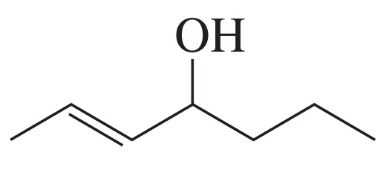
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
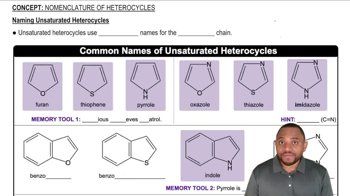
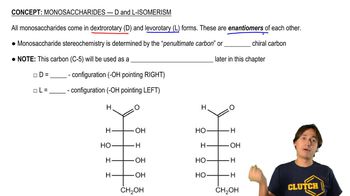

 4:28m
4:28mMaster How to name different types of double bonds or rings with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning