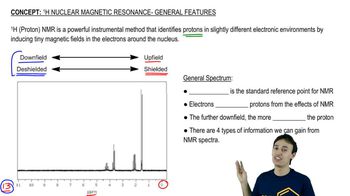
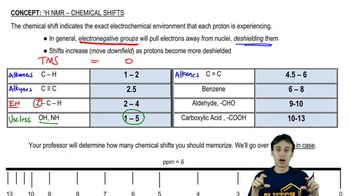
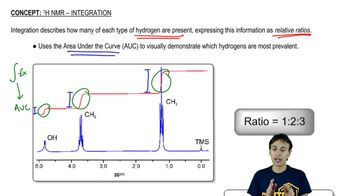
Propose chemical structures consistent with the following NMR spectra and molecular formulas. In spectrum (a), explain why the peaks around δ1.65 and δ3.75 are not clean multiplets, but show complex splitting.
(a) <IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: