Only after working Assessment 22.53, predict the product of the following reactions.
(b)
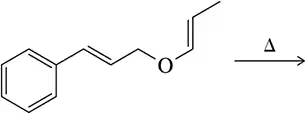
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: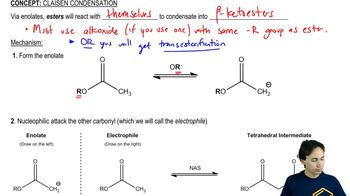

 6:08m
6:08mMaster Definition of Claisen Rearrangement with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning