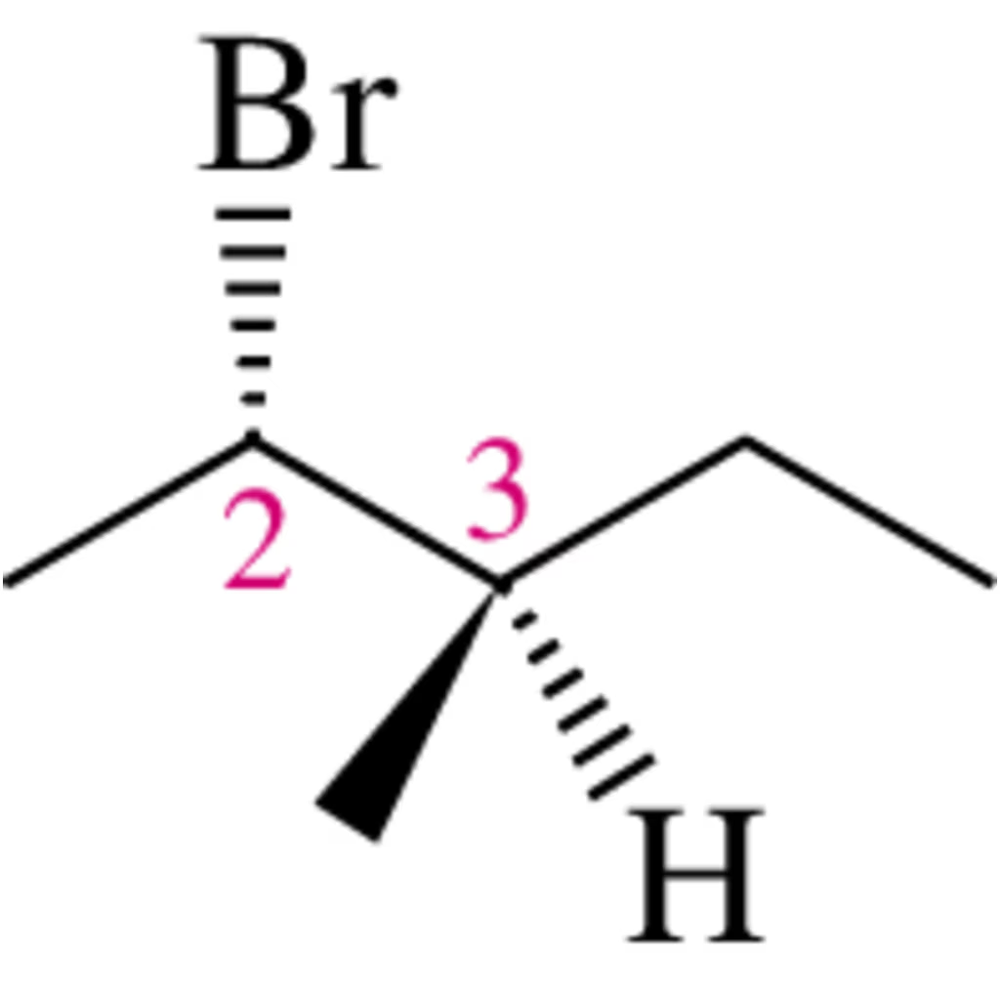
Looking down the indicated bond, show the three most stable conformations and choose the one that is most stable. Be sure that the first Newman projection you show is the one you see initially (before rotation). [Why should none of your three Newman projections show eclipsed conformations?]
(b) <IMAGE>