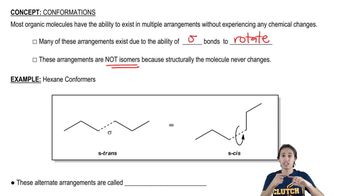
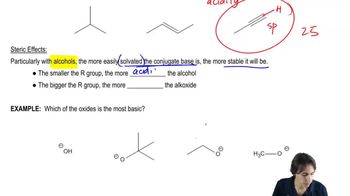
Given the following structures, show the Newman projection that would result from looking down the indicated bond in the direction shown. [Orient yourself as if you were the eyeball looking down the bond. Some of the examples have been partially completed for you to fill in the rest.]
(b) <IMAGE>