The Ka of phenylacetic acid is 5.2 × 10−5, and the pKa of propionic acid is 4.87.
a. Calculate the pKa of phenylacetic acid and the Ka of propionic acid.
b. Which of these is the stronger acid? Calculate how much stronger an acid it is.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: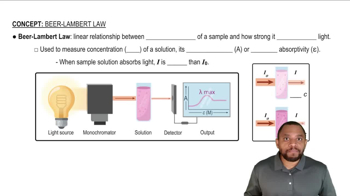

 9:36m
9:36mMaster The 12 pKa values you want to memorize (because they are important!). with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning