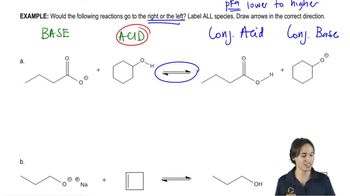
Given the structure of ascorbic acid (vitamin C):
(c) Predict which proton in ascorbic acid is the most acidic.
(d) Draw the form of ascorbic acid that is present in the body (aqueous solution, pH = 7.4)
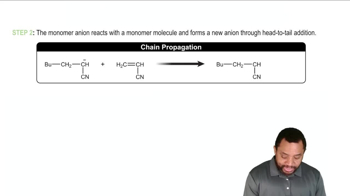
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
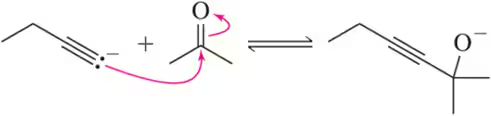
Verified video answer for a similar problem: