Draw the products of the following reactions. If the products can exist as stereoisomers, show which stereoisomers are formed.
b.
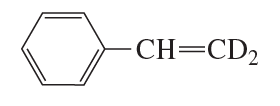
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 6:32m
6:32mMaster General properties of acid-catalyzed hydration. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning