Multiple Choice
What is the primary function of NADH in cellular metabolism?
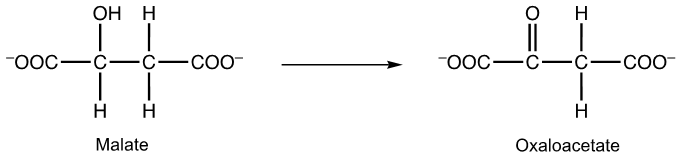
oxidation, NAD+
oxidation, NADH
reduction, NAD+
reduction, NADH
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
 2:2m
2:2mMaster Coenzymes in Metabolism Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning
