What dienes and dienophiles would react to give the following Diels–Alder products?
(a)
(b)
(c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: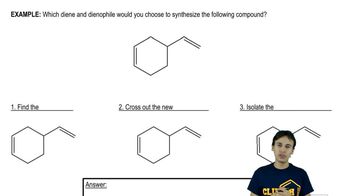
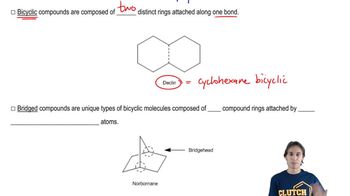


 4:02m
4:02mMaster Diels-Alder Retrosynthesis with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning