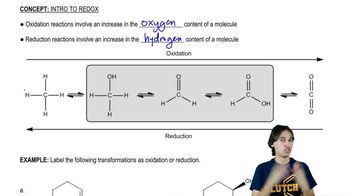
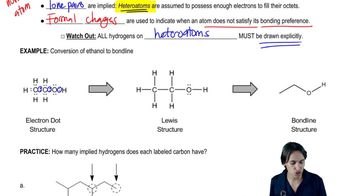
Predict the product(s) that would result when molecules (a)–(p) are allowed to react under the following conditions: (xi) HOCl, H₂O (xii) HIO₄ If no reaction occurs, write 'no reaction.'
(c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: