In each pair,
(i) choose the compound that is most soluble in water.
(ii) Within each pair, which is most soluble in nonpolar solvents?
(a)
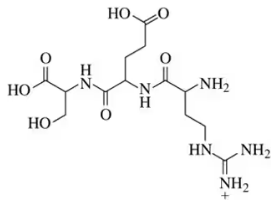
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 1:47m
1:47mMaster Understanding “like dissolves like”. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning