Predict the approximate bond angles for
c. the H—C—N bond angle in (CH3)2NH.
d. the H—C—O bond angle in CH3OCH3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: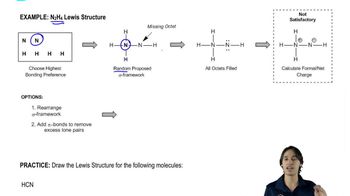
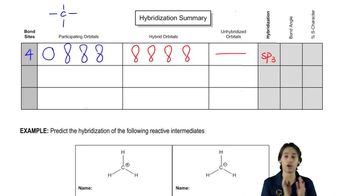
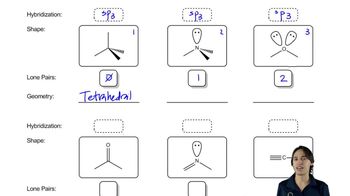

 7:44m
7:44mMaster Molecular Geometry Explained. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning