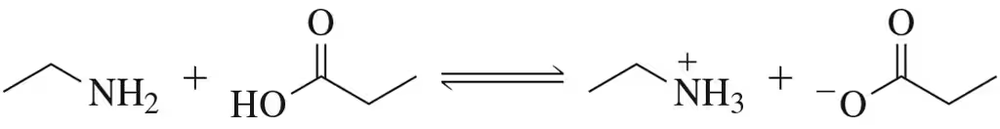
Using pKa values for the conjugate acids of the bases on each side of the reaction arrow, identify which side of the equilibrium would be favored in the following hypothetical reactions.
(c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 1:46m
1:46mMaster Why we use pKa instead of pH. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning