Multiple Choice
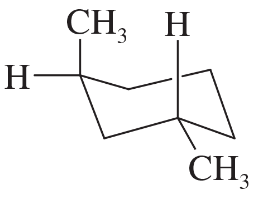
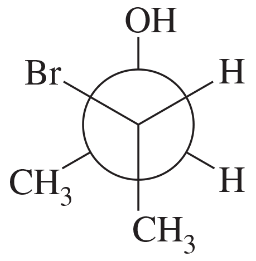
What is the relationship between these two molecules? The second molecule has the following structure: A 6-carbon hexagonal ring is in a vertical orientation with C 1 occupying the topmost vertex. A double bond is present between C 3 and C 4. C 2 is wedge bonded to O H." />