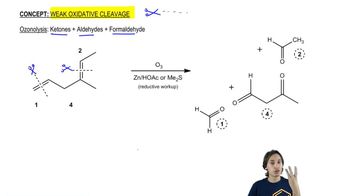
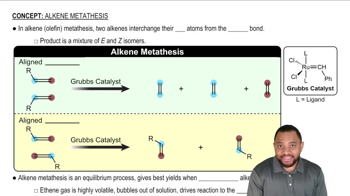
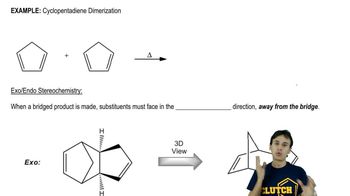
Professor Patrick Dussault (University of Nebraska at Lincoln) has developed an alternative to the standard two-step ozonolysis procedure requiring reduction of the ozonide in a second step. He uses 2 to 3 equivalents of pyridine, a mildly basic organic solvent, in a one-step process (Organic Letters, 2012, 14, 2242). Show the products you expect from the following examples.
(c)
(d)