In each part, rank the compounds in order of increasing rate of nucleophilic attack at C=O by a strong nucleophile like methoxide.
(a)
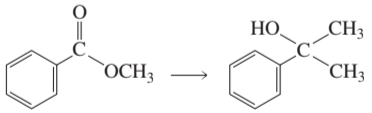
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 9:32m
9:32mMaster NAS - The Three Rules with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning