Show how you would convert 2-methylcyclopentanol to the following products. Any of these products may be used as the reactant in any subsequent part of this problem.
(g) 2-methylcyclopentyl acetate
(h) 1-bromo-1-methylcyclopentane
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
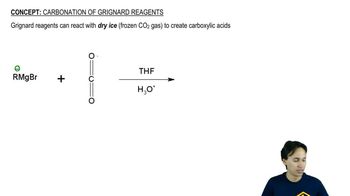
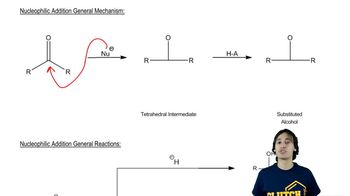

 9:32m
9:32mMaster NAS - The Three Rules with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning