Textbook Question
Which of the reactions studied in this chapter result in oxidation of the organic molecule? Justify your answer.
(d)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: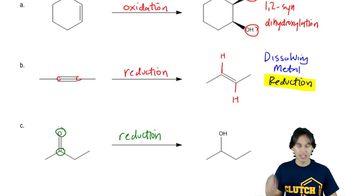
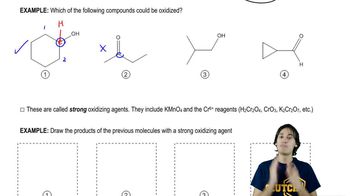
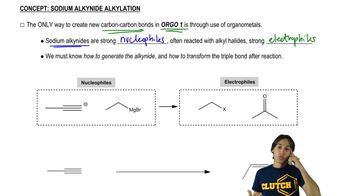

 6:02m
6:02mMaster General Features of Redox with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning