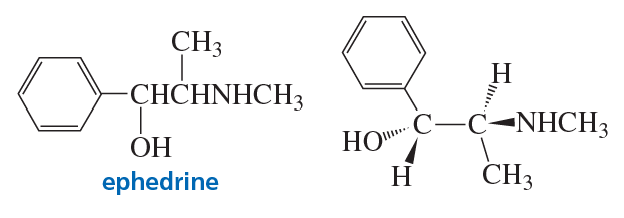
Draw the enantiomer, if any, for each structure.
(a)
(b)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 3:51m
3:51mMaster Determining when molecules are different. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning