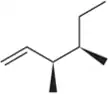
Predict the major product when each reagent reacts with ethylene oxide.
(d) PhNH2 (aniline)
(e) KCN (potassium cyanide)
(f) NaN3 (sodium azide)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 4:34m
4:34mMaster Acid-Catalyzed Epoxide Ring-Opening with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning