Draw the two chair conformers for each of the following and indicate which conformer is more stable:
b. trans-1-ethyl-2-methylcyclohexane
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: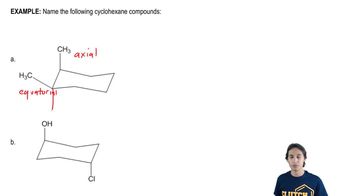

 4:02m
4:02mMaster Equatorial Preference with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning