Show an arrow-pushing mechanism for reactions 1–4 in Figure 9.37.
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: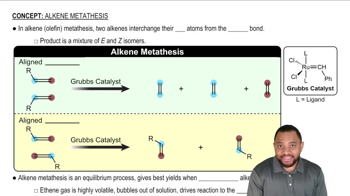


 4:34m
4:34mMaster Acid-Catalyzed Epoxide Ring-Opening with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning