Multiple Choice
Why is it important to have a standardized system like IUPAC for naming organic compounds?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: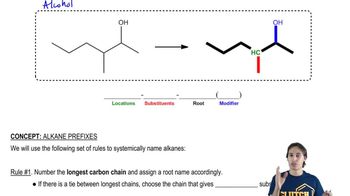


 3:43m
3:43mMaster The different parts of an IUPAC name with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning