Predict the alkyne and reactants you might use to make the following haloalkenes. [Providing the reactant and the reagent is how we start thinking about synthesis.]
(a)
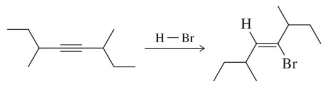
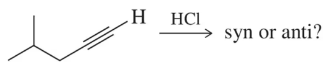
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 1:01m
1:01mMaster General properties of double addition reactions to alkynes. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning