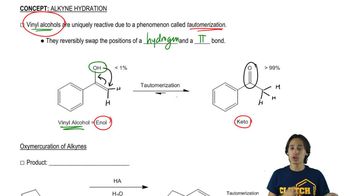
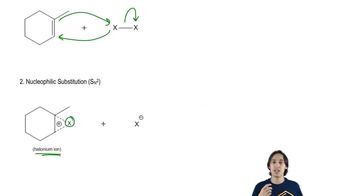
The addition of H―X to alkynes has been shown to occur predominately via anti addition:
Two chemists disagreed on whether or not anti addition would happen on terminal alkynes as well. Suggest an experiment through which you could resolve this dispute.