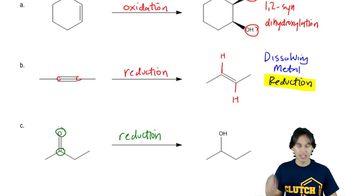
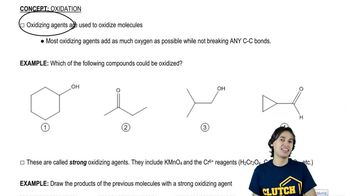
Show how Wittig reactions might be used to synthesize the following compounds. In each case, start with an alkyl halide and a ketone or an aldehyde.
(c) Ph–CH=CH–CH=CH–Ph
(d)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: