Draw the major elimination product that would be obtained from each of the following reactants with a strong base and with a weak base:
a.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: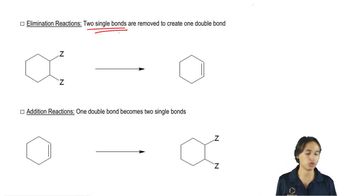


 2:27m
2:27mMaster Overview of the flowchart. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning