For each of the given species:
a. Draw its Lewis structure.
b. Describe the orbitals used by each carbon atom in bonding and indicate the approximate bond angles.
1. H2CO2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: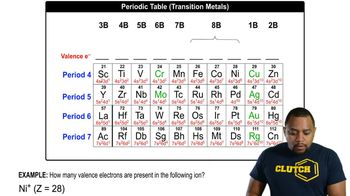
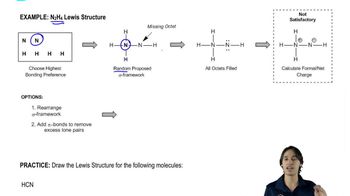


 3:49m
3:49mMaster How to use Organic Chemistry to make Lewis Structures easier. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning