For each of the following compounds, draw the important resonance forms. Indicate which structures are major and minor contributors or whether they have the same energy.
(e) [CH3C(OH)2]+
(f) [CH2CHNH]–
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: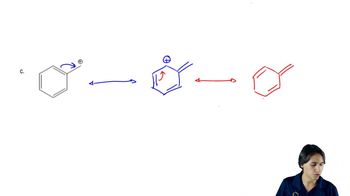
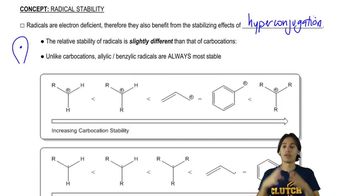
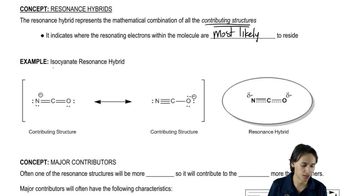

 3:34m
3:34mMaster The rules you need for resonance: with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning