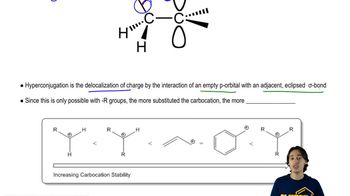
What are the products of the following reactions, assuming that one equivalent of each reagent is used in each reaction? Disregard stereoisomers.
a.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: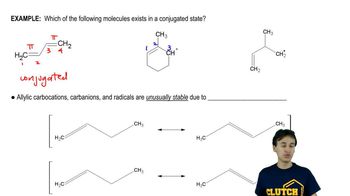


 12:6m
12:6mMaster Conjugated Hydrohalogenation - General Mechanism with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning