Draw complete Lewis structures, including lone pairs, for the following compounds.
(g)
(h)
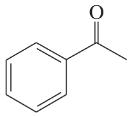
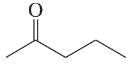
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: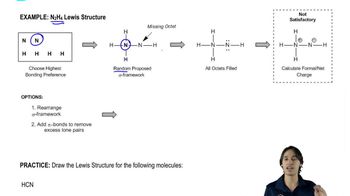


 3:49m
3:49mMaster How to use Organic Chemistry to make Lewis Structures easier. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning