Textbook Question
For each alkane, which monobrominated derivatives could you form in good yield by free-radical bromination?
a. Cyclopentane
b. Methylcyclopentnae
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: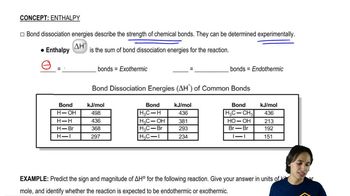
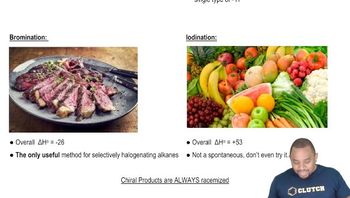

 1:08m
1:08mMaster Radical selectivity:Alcoholics Anonymous Version with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning