How could the following compounds be prepared using an alkene as one of the starting materials?
b.
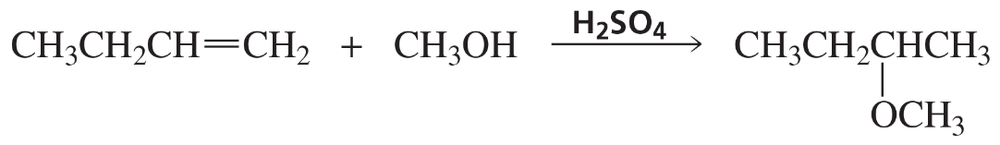
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:25m
4:25mMaster The Mechanism of Alkoxylation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning