Write structural formulas for the following compounds (includes both old- and new-style names).
g. 5,5-dibromo-4-phenylcyclooct-1-yne
h. (E)-6-ethyloct-2-en-4-yne
i.1,4-heptadiyne
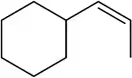
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: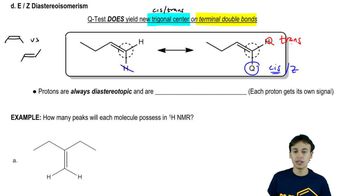

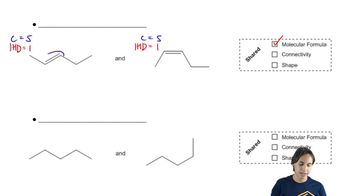

 4:28m
4:28mMaster How to name different types of double bonds or rings with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning