Predict the dehydrohalogenation product(s) that result when the following alkyl halides are heated in alcoholic KOH. When more than one product is formed, predict the major and minor products.
(d)
(e)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: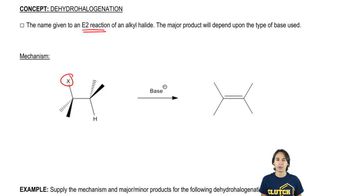



 3:02m
3:02mMaster The dehydrohalogenation mechanism. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning