Paying close attention to the stereochemical outcome, predict the product of these elimination reactions.
(d)
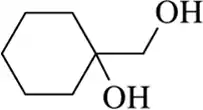
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 0:38m
0:38mMaster Intro to Substitution/Elimination Problems with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning