Predict the major products when the following compounds are irradiated by light and treated with (1) 1 equivalent of Br2 and (2) excess Br2.
(a) isopropylbenzene
(b)
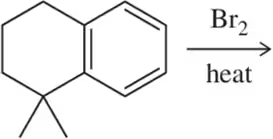
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 6:14m
6:14mMaster Side-Chain Halogenations with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning