Textbook Question
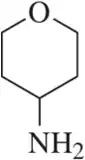
Draw in all missing lone pairs for the following molecules.
(c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 2:14m
2:14mMaster What is a valence electron? with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning