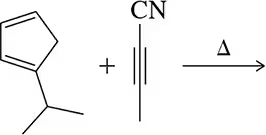
Figure 22.16(a) <IMAGE> shows a unique example where the Diels–Alder reaction gives a single product (no enantiomers) regardless of whether the diene attacks the dienophile from the top or bottom.
(a) Show the product of the diene attacking from the bottom and confirm that the same product is obtained.
(b) What is special about this product that makes this true?