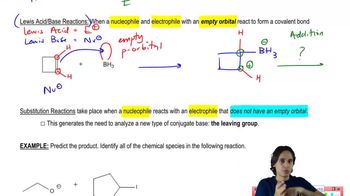
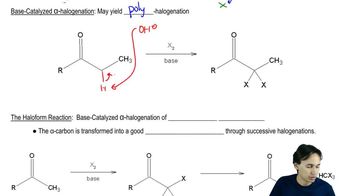
Suppose we have some optically pure (R)-2-butyl acetate that has been "labeled" with the heavy 18O isotope at one oxygen atom as shown.
(b) Repeat part (a) for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of this compound.
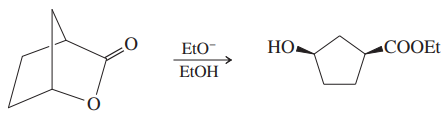
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: