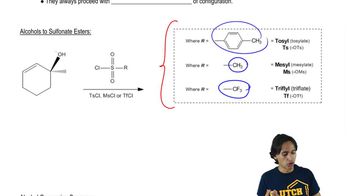
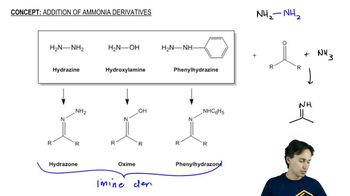
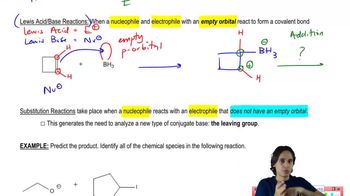
Show how to synthesize the following amines from the indicated starting materials by reductive amination.
(a) benzylmethylamine from benzaldehyde
(b) N-benzylpiperidine from piperidine
(c) N-cyclohexylaniline from cyclohexanone
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: