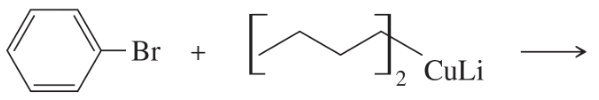
Furan undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution more readily than benzene; mild reagents and conditions are sufficient. For example, furan reacts with bromine to give 2-bromofuran.
b. Explain why furan undergoes bromination (and other electrophilic aromatic substitutions) primarily at the 2-position.